Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
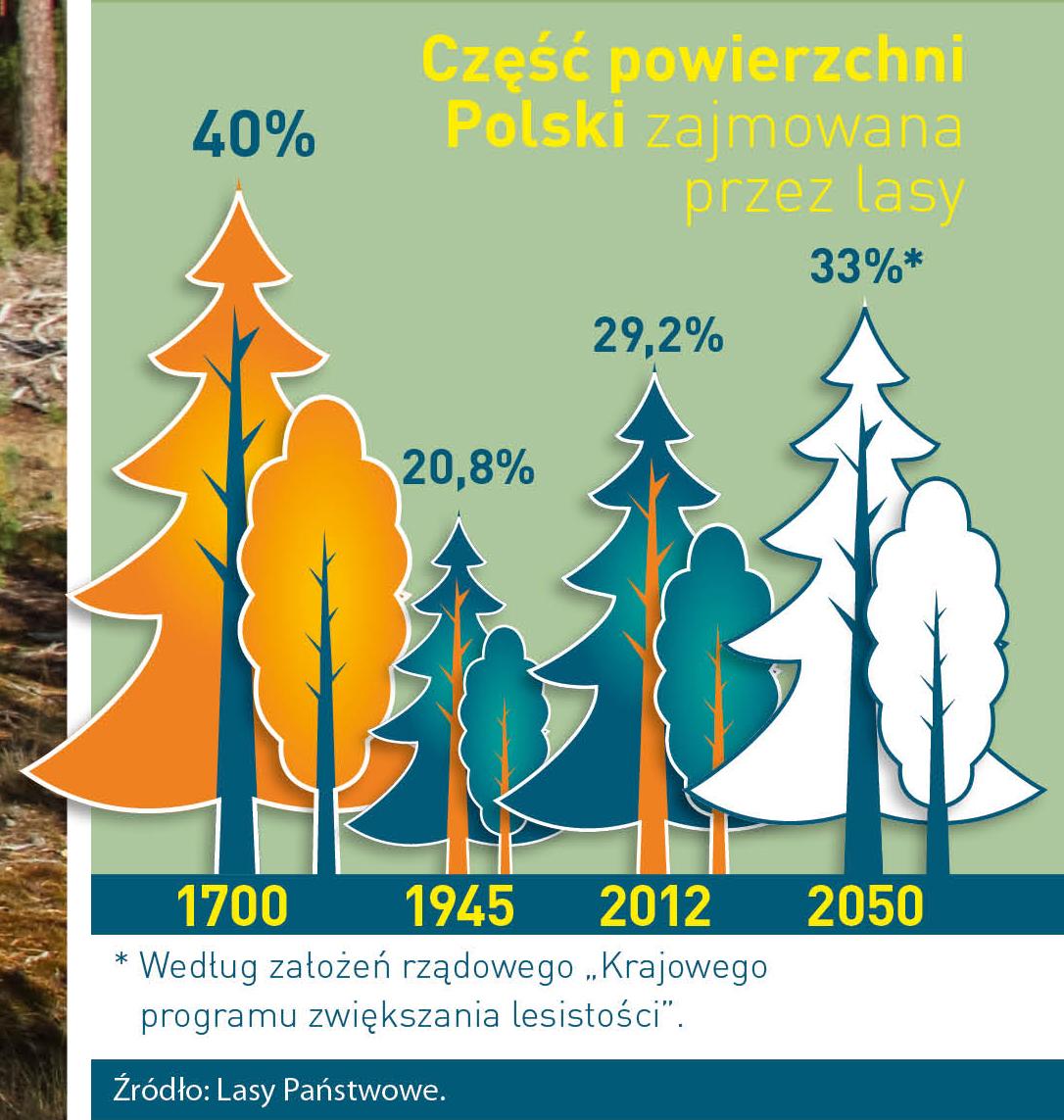
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Ścieżki edukacyjne
Ścieżki edukacyjne
Opis ścieżek edukacyjnych
Ścieżka „Szymocice"
Ścieżka zlokalizowana jest w leśnictwie Szymocice, a jej długość wynosi około 1,5 km i wiedzie ona przez oddział nr 257 obrębu leśnego Kuźnia Raciborska. Na jej trasie umieszczono 30 tablic edukacyjnych.
Ścieżka została podzielona na cztery bloki tematyczne
- Leśny mini świat – świat owadów dla najmłodszych
-
Część dendrologiczna – zawierająca między innymi informacje o dziewięciu gatunkach drzew leśnych
- Funkcje lasu
- Tropami zwierząt – przedstawia jedenaście gatunków zwierząt, których tropy i ślady można spotkać w tutejszej okolicy. Na trasie ścieżki ulokowano dwa miejsca odpoczynku, gdzie można odpocząć i nabrać „leśnej" energii.
Zachęcamy do korzystania z darmowej drzewo terapii, bowiem przebywanie pośród swobodnie rosnących drzew, przytulanie się do nich, głaskanie, obejmowanie i wąchanie powoduje, że lepiej wypoczywamy. Substancje zawarte w liściach, kwiatach i korze mają cenne właściwości – poprawiają samopoczucie i dodają sił.
Leśna Dydaktyczna Ścieżka Rowerowa
Ścieżka rowerowa prowadzi przez fragment kompleksu leśnego zwanego Lasami Rudzkimi, w części „ocierając się" o teren wielkoobszarowego pożarzyska z 1992 r. Jej długość wynosi 16 km, a na jej trasie rozmieszczonych jest 35 tablic tematycznych.
1. Witamy na ścieżce rowerowej
2. Dlaczego las jest taki ważny?
3. Ile mamy lasów w Polsce?
4. Sposoby zagospodarowania lasu
5. Drzewa leśne
6. Rola mrówek w ekosystemie leśnym
7. Zbiornik wodny i jego rola w lesie
8. Stare drzewa – mały ekosystem
9. Wielki pożar lasu z sierpnia 1992 r.
10. Owady w lesie
11. Pułapki feromonowi
12. Stara grobla cysterska
13. System ochrony p.poż.
14. Wieża obserwacyjna „Borowiec"
15. Nisze pokarmowe ptaków
16. Gospodarka łowiecka
17. Pielęgnowanie lasu
18. Uroczysko „Orły"
19. Podział powierzchniowy lasu
20. Ochrona lasu
21. Paśnik
22. Selekcja genetyczna w leśnictwie
23. Dary lasu
24. Ptasi budzik
25. Przebudowa drzewostanów
26. Geomorfologia terenu
27. Ochrona gatunkowa roślin
28. Grzyby w lesie
29. Mikoryza
30. Stara droga
31. Uroczysko „Dziewicze Groby"
32. Powalone drzewa
33. Cięcia pielęgnacyjne
34. Fazy rozwoju drzewostanu
35. Pożegnanie
Ścieżka przyrodniczo leśna w leśnictwie Stanica
Ścieżka zlokalizowana jest w przypałacowym parku Pocysterskiego Zespołu Klasztorno-Pałacowego w Rudach, którego powierzchnia wynosi 95ha. Jej długość wynosi 1,5 km i prowadzi przez ogród w stylu angielskim, gdzie zobaczyć można wiele drzew o rozmiarach pomnikowych, kompozycje ogrodowe oraz zespoły łąkowe. Na jej trasie znajduje się wiele tablic opisujących faunę i florę Nadleśnictwa Rudy Raciborskie.
Leśna ścieżka Dydaktyczna na terenie leśnict wa Lubieszów w woj. opolskim
wa Lubieszów w woj. opolskim
Ścieżka zlokalizowana jest w niedużej odległości od kopalni piasku „Kotlarnia" oraz wyrobiska w Dziergowicach, a jej niewielka część biegnie granicą pożarzyska. Ścieżka tworzy pętle o długości około 1 km i wzbogacona jest tablicami edukacyjnymi o tematyce biologii drzew, łowieckiej oraz p.poż. Przy ścieżce znajduje się także drewniana wiata mogąca pomieścić około 30 osób.
Źródło map: http://mapa.katowice.lasy.gov.pl/


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański